Keywords
Abstract
Introduction: Prognostication is essential for risk stratification in the ICU. The SOFA, APACHE II, and SAPS II scores are widely used severity scoring systems, although their renal components differ. Given the association of acute kidney injury (AKI) with higher morbidity and mortality, this study evaluated these scoring systems and identified which renal component best predicts ICU outcomes. Such an insight can enhance the precision of risk assessment in critically ill patients.
Methods: A retrospective observational cohort study was conducted involving all patients admitted to the Sultan Ahmad Shah Medical Centre ICU. SOFA, APACHE II, and SAPS II scores, along with their individual components, were calculated within the first 24 hours of ICU admission.
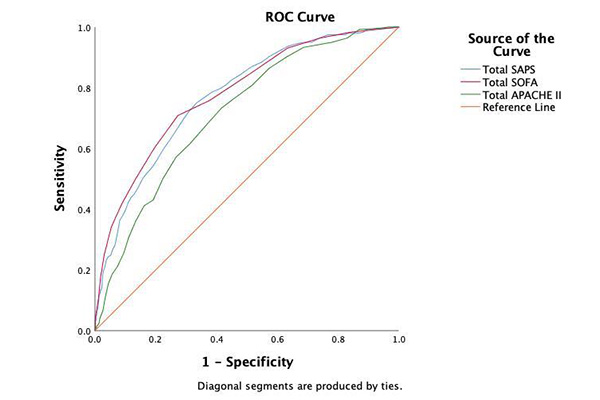
Results: Of the 1,513 patients analysed, 360 (23.8%) died in hospital. The SOFA score had the highest predictive accuracy for hospital mortality (AUC 0.78), followed by SAPS II (0.77) and APACHE II (0.72). Optimal cut-off points were identified for practical application. The renal components of the SOFA and SAPS II had similar AUCs of 0.64, while APACHE II’s renal component was lower (0.62). Findings were consistent in the AKI subgroup.
Conclusions: The SOFA score outperformed APACHE II and SAPS II in predicting hospital mortality in critically ill patients. The renal components of the SOFA and SAPS II scores were more predictive than the that of APACHE, likely due to the inclusion of urine output criteria. Future multicentre studies using raw patient-level data are needed to develop a robust prognostic model tailored to our local ICU population.
References
Friedrich JO, Wilson G, Chant C. Long-term outcomes and clinical predictors of hospital mortality in very long stay intensive care unit patients: A cohort study. Crit Care. 2006;10(2):R56. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc4888
Wong DT, Knaus WA. Predicting outcome in critical care: the current status of the APACHE prognostic scoring system. Can J Anaesth. 1991;38(3):374–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03007629
Le Gall J-R. A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA. 1993;270(24):2957–2963. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1993.03510240069035.
Vincent J-L, de Mendonça A, Cantraine F, et al. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: Results of a multicenter, prospective study. Crit Care Med. 1998;26(11):1793–1800.
Ralib A, Nanyan S, Ramly N, Har L, Cheng T, Mat Nor M. Acute kidney injury in Malaysian intensive care setting: Incidences, risk factors, and outcome. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018;22(12):831–835. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijccm.IJCCM_193_18
Vincent J-L, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(7):707–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709751.
Moreno R, Vincent J-L, Matos R, et al. The use of maximum SOFA score to quantify organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care: Results of a prospective, multicentre study. Intensive Care Med. 1999;25(7):686–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050931.
Md Ralib A, Said@Ahmad NA, Ramly NF, Nanyan S, Ismail MN, Mat Nor MB. Serial evaluation of Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score in predicting 1-year mortality in critically ill patients. IIUM Med J Malaysia. 2022;21(3). https://doi.org/10.31436/imjm.v21i3.2029
Nfor TK, Walsh TS, Prescott RJ. The impact of organ failures and their relationship with outcome in intensive care: Analysis of a prospective multicentre database of adult admissions. Anaesthesia. 2006;61(8):731–738. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2006.04707.x
Ferreira FL. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA. 2001;286(14):1754–1758. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.286.14.1754
Bota DP, Melot C, Ferreira FL, Ba VN, Vincent JL. The Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (MODS) versus the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score in outcome prediction. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28(11):1619–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1491-3
Khwannimit B, Bhurayanontachai R, Vattanavanit V. Comparison of the accuracy of three early warning scores with SOFA score for predicting mortality in adult sepsis and septic shock patients admitted to intensive care unit. Heart Lung. 2019;48(3):240–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrtlng.2019.02.005
Tee YS, Fang HY, Kuo IM, Lin YS, Huang SF, Yu MC. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score is reliable for predicting mortality in acute severe pancreatitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(7):e9654. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000009654
Janssens U, Graf C, Graf J, et al. Evaluation of the SOFA score: a single-center experience of a medical intensive care unit in 303 consecutive patients with predominantly cardiovascular disorders. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26(8):1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340051316
Demandt AMP, Geerse DA, Janssen BJP, Winkens B, Schouten HC, van Mook WNKA. The prognostic value of a trend in modified SOFA score for patients with hematological malignancies in the intensive care unit. Eur J Haematol. 2017;99(4):315–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.12919
Wang H, Kang X, Shi Y, et al. SOFA score is superior to APACHE II score in predicting the prognosis of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy. Ren Fail. 2020;42(1):638–645. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2020.1788581
Gong Y, Ding F, Zhang F, Gu Y. Investigate predictive capacity of in-hospital mortality of four severity score systems on critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. J Investig Med. 2019;67(8):1103–1109. https://doi.org/10.1136/jim-2019-001003.
Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120(4):c179–c183. https://doi.org/10.1159/000339789
Md Ralib A, Pickering JW, Shaw GM, Endre ZH. The urine output definition of acute kidney injury is too liberal. Crit Care. 2013;17(3):R112. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc12784
Quan S, Pannu N, Wilson T, et al. Prognostic implications of adding urine output to serum creatinine measurements for staging of acute kidney injury after major surgery: A cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(12):2049–2056. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfw374
Dao CX, Dang TQ, Luong CQ, et al. Predictive validity of the sequential organ failure assessment score for mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Vietnam. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):7406. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-12566-0