Keywords
Abstract
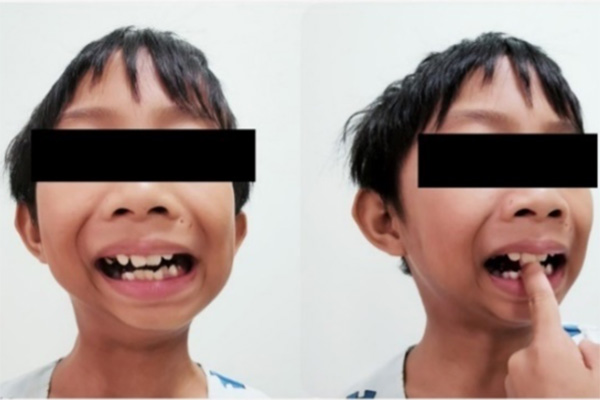
Airway management in the paediatric population is known to be challenging due to its unique anatomical and physiological differences. Maxillofacial injuries further complicate airway management. To date, there is limited evidence to support the technique of airway management and the choice of drugs used in the paediatric population. This case report aims to describe the technique of conscious sedation using dexmedetomidine and ketamine to perform an awake fibreoptic intubation in the case of an 8-year-old boy with limited mouth opening due to a temporo-mandibular joint ankylosis secondary to childhood trauma. The endpoint of this case report showed that this technique proved effective with a good margin of safety in this paediatric patient with an airway concern. Further studies are needed to validate this observation.
References
Jagannathan N, Sohn L, Fiadjoe JE. Paediatric difficult airway management: what every anaesthetist should know! Br J Anaesth. 2016 Sep;117 Suppl 1:i3-i5. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aew054
Beck JI. Beck, Anaesthesia for cosmetic and functional maxillofacial surgery, Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care and Pain. 2014;14(1): 38–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkt027
Roberts S. Paediatric bronchoscopy. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care and Pain. 2005;5(2):41–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaceaccp/mki015
Prasad Y. The Difficult Paediatric Airway. Paediatric Anaesthesia, Tutorial 250, World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists. Available from: https://resources.wfsahq.org/atotw/the-difficult-paediatric-airway-anaesthesia-tutorial-of-the-week-250/
Walker RW, Ellwood J. The management of difficult intubation in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2009 Jul;19 Suppl 1:77-87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9592.2009.03014.x
Raval CB, Rashiduddin M. Airway management in patients with maxillofacial trauma - A retrospective study of 177 cases. Saudi J Anaesth. 2011 Jan;5(1):9-14. https://doi.org/10.4103/1658-354X.76476
Sharma A, Dwivedi D, Sharma RM. Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis: “A Pediatric Difficult Airway Management”. Anesth Essays Res. 2018 Jan-Mar;12(1):282-284. https://doi.org/10.4103/aer.AER_122_17
Babl FE, Goldfinch C, Mandrawa C, Crellin D, O’Sullivan R, Donath S. Does Nebulized Lidocaine Reduce the Pain and Distress of Nasogastric Tube Insertion in Young Children? A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Pediatrics. 2009 May 26;123(6):1548–55. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-1897
Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of alpha2 -adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology. 2000 Nov;93(5):1345-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200011000-00030
He XY, Cao JP, He Q, Shi XY. Dexmedetomidine for the management of awake fibreoptic intubation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 19;2014(1):CD009798. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009798.pub2
Tobias JD. Dexmedetomidine and ketamine: an effective alternative for procedural sedation? Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012 Jul;13(4):423-7. https://doi/10.1097/PCC.0b013e318238b81c
Perioperative Applications of Dexmedetomidine [Internet]. WFSA Resource Library. Available from: https://resources.wfsahq.org/atotw/perioperative-applications-of-dexmedetomidine-atotw-469/